Accessibility Options:
****The University of Miami is currently subscribed to Scopus/SciVal, Web of Science/InCites, and Academic Analytics****
Scopus - Scopus is a curated database featuring abstracts and citations, offering enriched data and interlinked scholarly literature from over 7,000 publishers across disciplines. Scopus is the primary data source for SciVal.
- Scival - SciVal is an advanced analytics solution, built on a core of Scopus data. This platform allows the evaluation of any research field as well as the research performance of individuals, research groups, departments, institutions, and countries. SciVal applies advanced data science and techniques to provide insights from research information to support decision making.
SciVal allows for the ability to:
- Visualize and understand research performance
- Evaluate, benchmark & monitor progress
- Build strong teams and partnerships
- Investigate developments and trends in research
- View impact which can showcase how research informs policy
- Review grants information and advance funding strategies
Web of Science (WOS) – WOS incorporates citation indexes which include details of scholarly journal articles from all academic subject areas, details of conference proceedings from science and technology conferences and details of book chapter references from selected science, social science and humanities books. WOS includes Journal Citation Reports (JCR), InCites, and Essential Science Indicators, through the InCites platform. These resources can be used for identifying Journal Impact Factors (JIF) and institutional performance rankings. WOS is the primary data source for InCites.
- InCites – InCites allows for the analysis of data from the Web of Science Core Collection to make decisions about research programs. Provides information that may assist in strategic planning, benchmarking against peers, demonstration of funding outcomes and optimization of collaborations.
InCites allows for the ability to:
- Assess research and researchers to understand impact and establish strategies for the future
- Analyze past awarded grants to inform strategic proposal development for new funding
- Identify top contributors in relevant research areas to build expert teams and strategic partnerships
- Ability to demonstrate contributions to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Academic Analytics - "Academic Analytics compiles multi-faceted data on individual scholar research productivity, aggregates individual data to the academic unit level, and benchmarks academic unit data against peer units across the country. Academic Analytics is unique among faculty activity solutions – they match activity data to the individual scholar and aggregate scholars into custom groups– centers, programs, departments and more – with a robust set of filtering options to create peer groups and time windows for benchmarking.” Keep in mind that the portal access should be focused on central administrators, administrative staff, Deans/Associate Deans, and chairs/directors. If you would like to become a credentialed user to the portal or require additional information about Academic Analytics, please contact the Office of Institutional Research & Strategic Analytics at umdata@miami.edu.
Other Available Platforms:
Lens - The Lens aggregates metadata and full text, combines unique content sets (scholarly works, patents and biological sequences) with management tools at its core. The Lens offers all registered users a Personal Account with a Professional Workspace, providing access to tools and features on the Lens.org platform, and built on open shareable metadata to support many use cases and use types across industry and the research and innovation sectors. Most of the Lens platform is open access with paid Institutional Accounts as an option. However, the University of Miami currently does not have access to the paid portion of Lens.
OpenAlex - OpenAlex indexes over 250M scholarly works from 250k sources, with extra coverage of humanities, non-English languages, and the Global South. The works are linked to 90M disambiguated authors and 100k institutions, that also include topic information, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), citation counts, and more. OpenAlex is an open platform and is the successor of Microsoft Academic Graph.
Scopus/SciVal:
CiteScore metrics - CiteScore metrics are a suite of indicators calculated from data in Scopus. Calculating the CiteScore is based on the number of citations to documents (articles, reviews, conference papers, book chapters, and data papers) by a journal over four years, divided by the number of the same document types indexed in Scopus and published in those same four years. CiteScore is calculated for the current year on a monthly basis until it is fixed as a permanent value in May the following year, permitting a real-time view on how the metric builds as citations accrue. Once fixed, the other CiteScore metrics are also computed and contextualize this score with rankings and other indicators to allow comparison.
Field Weighted Citation Impact (FWCI) - FWCI is the ratio of the total citations actually received by the denominator’s output, and the total citations that would be expected based on the average of the subject field.
Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP) - SNIP is a metric that intrinsically accounts for field-specific differences in citation practices. SNIP compares each journal’s citations per publication with the citation potential of its field, defined as the set of publications citing that journal. SNIP therefore measures contextual citation impact and enables direct comparison of journals in different subject fields, since the value of a single citation is greater for journals in fields where citations are less likely, and vice versa.
SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) - SJR is based on the concept of a transfer of prestige between journals via their citation links. Drawing on a similar approach to the Google PageRank algorithm - which assumes that important websites are linked to from other important websites - SJR weights each incoming citation to a journal by the SJR of the citing journal, with a citation from a high-SJR source counting for more than a citation from a low-SJR source. Like CiteScore, SJR accounts for journal size by averaging across recent publications and is calculated annually.
Web of Science/InCites:
Journal Citation Reports (JCR) - JCR provides quantitative tools for ranking, evaluating, categorizing, and comparing journals. Journal Impact Factor (JIF) is one of these tools and measures the frequency with which the “average article” in a journal has been cited in a particular year or period. The annual JCR impact factor is a ratio between citations and recent citable items published. Thus, the impact factor of a journal is calculated by dividing the number of current year citations to the source items published in that journal during the previous two years
Essential Science Indicators (ESI) - ESI is an analytical tool that helps identify top-performing research in Web of Science Core Collection. ESI surveys more than 11,000 journals from around the world to rank authors, institutions, countries, and journals in 22 broad fields based on publication and citation performance. Data covers a rolling 10-year period and includes bimonthly updates to rankings and citation counts.
- Examines the research performance of top-ranking institutions, countries, journals, authors, and papers in each of the 22 research fields in Essential Science Indicators.
- Compares the citation performance of a paper with that of its peers by both publication period and field.
- Identifies trends and emerging areas of research in the sciences and social sciences.
Category Normalized Citation Impact (CNCI) - CNCI is a calculation that divides the actual count of citing items by the expected citation rate for documents with the same document type, year of publication and subject area. When a document is assigned to more than one subject area an average of the ratios of the actual to expected citations is used.
Journal Normalized Citation Impact (JNCI) - JNCI is an indicator that normalizes the citation rate for the journal in which the document is published. The JNCI of a single publication is the ratio of the actual number of citing items to the average citation rate of publications in the same journal in the same year and with the same document type. The JNCI for a set of publications is the average of the JNCI for each publication.
The JNCI indicator can:
- Reveal information about the performance of a publication (or a set of publications) in relation to how other researchers perform when they publish their work in a given journal (or a set of journals).
- Can provide the answers to questions, such as “How do my papers perform in the journals I publish?” If the numerical value of the JNCI exceeds one, then the assessed research entity is performing above average. If it is less than one, then it is performing below the average.
- Measure post–publication performance and that can reveal which research work exceeds average performance and therefore increases the citation rates of a journal.
Academic Analytics:
Scholarly Research Index (SRI) - SRI was developed to express the level of research activity across disciplines. The Scholarly Research Index can be applied at different levels; the level of individual faculty, units (programs or departments) within a university, and the overall performance of universities. The Index uses metrics that are independent of discipline values and of the portfolio of disciplines at universities.
The tools within Academic Analytics assist in analyzing data on the primary areas of scholarly accomplishment such as journal articles, citations, books, grants, conference proceedings, and awards from over 430,000 faculty members associated with more than 10,000 Ph.D. programs and 12,000 departments at 541 U.S. universities.
The data covers the past decade or longer and is configurable, enabling users to create custom peer groups, time windows, and custom weights for individual variables allowing for comparative analysis of scholarly activity across departments, programs, institutions and disciplines.
OpenAlex:
Field Weighted Citation Impact (FWCI) - FWCI is the ratio of the total citations actually received by the denominator’s output, and the total citations that would be expected based on the average of the subject field.
FAQs
What is Scopus and how is it related to SciVal?
Scopus is the primary data source for SciVal and includes abstracts and citations, enriched data and interlinked scholarly literature from over 7,000 publishers across disciplines. Using Scopus data, SciVal allows for an evaluation of research fields as well as the research performance of individuals, research groups, departments, institutions, and countries using the metrics tools available through both platforms.
What is Web of Science and how is it related to InCites?
Web of Science (WOS) is the primary data source for InCites. WOS data includes citation indexes with additional details of scholarly journal articles from all academic subject areas, details of conference proceedings from science and technology conferences and details of book chapter references from selected science, social science and humanities books. This data feeds InCites where analysis can be performed using a variety of metrics and tools.
What Research Analytics tools does the University of Miami have subscriptions too?
The University of Miami is currently subscribed to Scopus/SciVal, Web of Science/InCites, and Academic Analytics.
How can I access each Research Analytics platform?
All UM affiliated individuals can click the following links for Scopus and SciVal and create an account using UM credentials.
*Since Scopus/SciVal are both Elsevier products only one account needs to be created in one of the platforms.
All UM affiliated individuals can click the following links for Web of Science (WOS) and InCites and create an account using UM credentials.
*Since Web of Science (WOS) and InCites are both Clarivate products only one account needs to be created in one of the platforms.
All of the platforms and tools can also be accessed throughout this guide including the open platforms Lens and OpenAlex.
Access should be focused on central administrators, administrative staff, Deans/Associate Deans, and chairs/directors. If you would like to become a credentialed user to the portal or require additional information about Academic Analytics, please contact the Office of Institutional Research & Strategic Analytics at umdata@miami.edu.
What platforms are used for university rankings?
Ranking services that use Scopus/SciVal data in their rankings process include:
- U.S. News Best Colleges — National Universities rankings
- QS World University Rankings
- Times Higher Education World University Rankings
Ranking services that use Web of Science/InCites data in their rankings process include:
- Shanghai Ranking which includes the Academic Ranking of World Universities (AWRU) and Global Ranking of Academic Subjects (GRAS)
- CWTS Leiden Ranking
- Round University Ranking
What Research Analytics platform uses Journal Impact Factor (JIF)?
Journal Impact Factor (JIF) is only available through Web of Science/InCites and measures the frequency with which the “average article” in a journal has been cited in a particular year or period.
What is a Scopus ID? And why is it important?
Scopus ID is a unique 11-digit identifier assigned by the Scopus database to each author who has published in journals indexed by Scopus. A Scopus ID will allow you to manage and track the impact of your publications and citation metrics and link to co-authors and collaborators. Keeping your Scopus author ID up to date ensures that your work is correctly attributed and your metrics are reflective of your research outputs.
What is a Web of Science (WOS) Researcher ID? And why is it important?
Web of Science Researcher ID is a unique identifier assigned in Web of Science to each author who has published in journals indexed by WOS. Having a Web of Science Researcher ID helps solve author identity issues, ensure correct attribution between you and your publications in Web of Science, and add dynamic citation metrics from the Web of Science Core Collection and other missing metadata to publication records on your Publons profile, Web of Science, InCites, etc.
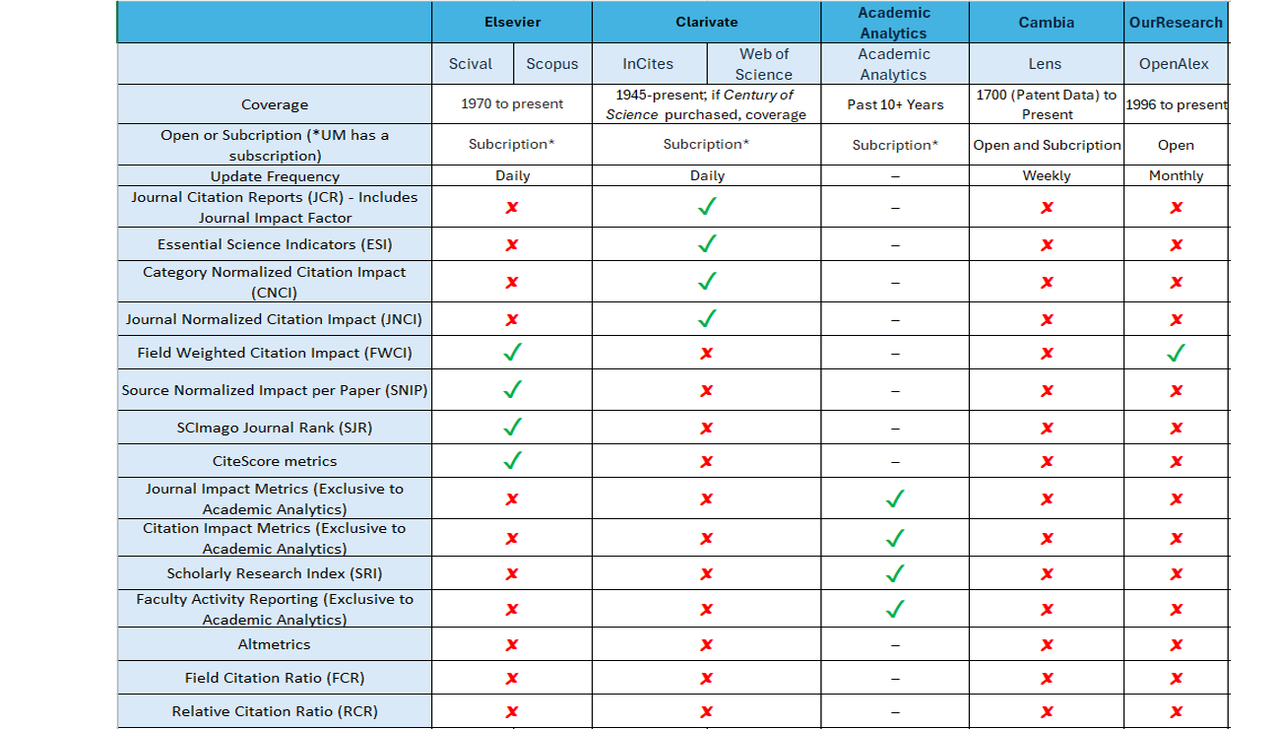
Summary Chart of Research Platforms and Related Metrics/Tools
Raising the Visibility & Impact of Your Research
- ORCID (Open Researcher and Contributor ID) is a registry of unique identifiers for researchers and scholars that is open, non-proprietary, transparent, mobile, and community-based. ORCID provides a universal persistent digital identifier that distinguishes you from every other researcher.
Use your ORCiD with your publications
- Your ORCID will be connected with Scholarship@Miami, the University of Miami Libraries’ research information hub & institutional repository. Having an ORCID will raise the level of discovery for your work and help us create a complete bibliographic record of your research.
Review your Scopus ID and consolidate (If necessary)
- Scopus ID is a unique 11-digit identifier assigned by the Scopus database to each author who has published in journals indexed by Scopus. A Scopus ID will allow you to manage and track the impact of your publications and citation metrics and link to co-authors and collaborators. Keeping your Scopus author ID up to date ensures that your work is correctly attributed and your metrics are reflective of your research outputs. You can access your Scopus ID by creating an account or signing in to the Scopus platform. Make sure you affiliation is University of Miami and you have one profile that includes your research. If you have more than one profile please consolidate all research into one.
Publish in OA Journals (While avoiding predatory journals)
- The University of Miami Libraries have established publishing agreements (some are pilot programs) which provide researchers with qualifying articles the possibility of APC funding. In addition, the University of Miami Libraries manages the Scholarship@Miami research repository which allows authors to publish green open access, if their author agreement allows. The Open Access Funding Guide provide the most up to date information and details for each agreement.
- The UM research guide on Predatory or Disreputable Publishers provides information on predatory journals and topics to be aware of as an author. In addition, The Choosing the Right Journal page assists in locating a reputable journal for your manuscript.
Create and keep up to date your People and Scholarship@Miami profiles
- People profiles are the official University of Miami profile and can be managed by the individual and the School/Colleges People Profile Manager. Additional information on how to access and manage your profile can be found on the "How Does the People Site Work?".
- Scholarship@Miami features profiles of all University of Miami faculty and affiliated researchers. These profiles include an author matching feature which will automatically populate profiles with citations and links to publications. Profiles also include research interests, activities, and grant information. You can access your profile by finding your profile in Scholarship@Miami and signing in using your Cane ID credentials.
Showcase your research through various outlets
- Present your work at conferences (local, regional, national, and international)
- Collaborate, connect and engage through social media platforms
Apply for grants
- The University of Miami Libraries currently has subscriptions to GrantForward and Foundation Directory to help assist in locating and applying to grants.